써먹는 웹개발
[Java] 9강 클래스와 객체 본문
09 클래스와 객체
1. 객체 지향 프로그래밍 (Object Oriented Programming)
- 객체지향프로그래밍이란, 조립식 프로그래밍이다. 객체를 조립하여 전체 프로그램을 만드는 것이다.
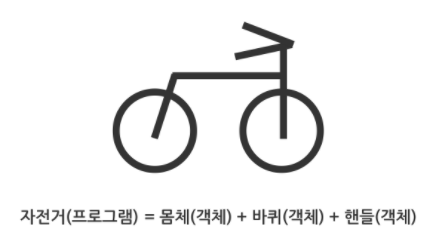
- 장점 3가지
1) 관리(유지 보수성) : 고장이 나도 해당 부분만 수리하면 된다.
2) 재사용성 : 조립식으로 프로그램을 만들면 다른 쪽에도 재사용이 가능하다.
3) 확장성 : 기능을 추가할 때, 만들어서 끼워 넣으면 된다.

2. 클래스와 객체
- 클래스는 객체를 만들기 위한 설계도이다.
객체의 또 다른 표현으로는 인스턴스가 있다. (인스턴스화 = 클래스로 객체를 만드는 것)
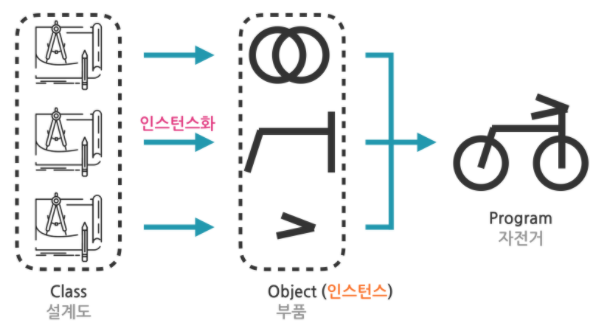
프로그램을 만들려면 여러 객체가 필요하다. 여러 객체를 만들려면 객체별 클래스가 필요하다.
결과적으로 프로그램을 만들기 위해서는 클래스를 잘 만들어야한다.
3. 클래스 설계 및 구현
- 클래스는 2 영역으로 나뉜다. 상태를 정의하는 필드와 동작을 정의하는 메소드이다.
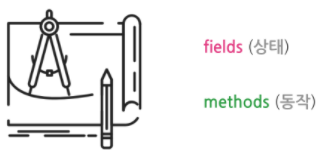
- 클래스를 도식화 한 것이 클래스 다이어그램이며,
클래스 다이어그램을 보고 코드를 작성할 줄 알아야 한다.

4. 개념 실습
1. 클래스 구현하기
/* Main 클래스 */
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Dog 객체 생성
Dog d = new Dog();
// Dog 객체 필드 값 출력
System.out.printf("이름: %s\n", d.name);
System.out.printf("품종: %s\n", d.breeds);
System.out.printf("나이: %s\n", d.age);
}
}
/* Dog 클래스 */
class Dog {
/* 1. 필드 영역을 작성하시오. */
String name = null;
String breeds = null;
int age = 0;
/* 2. 메소드 영역을 추가하시오. */
void wag() {
System.out.println("살랑살랑 꼬리를 친다!");
}
void bark() {
System.out.println("멍멍! 개가 짖습니다!");
}
}
2. 객체 생성과 필드 값 변경
/* CatTest 클래스 */
public class CatTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Cat 객체 생성
Cat c = new Cat();
/* 1. 객체의 필드 값을 변경하시오. */
c.name = "네로";
c.breeds = "페르시안";
c.age = 3;
// Dog 객체 필드값 출력
System.out.printf("이름: %s\n", c.name);
System.out.printf("품종: %s\n", c.breeds);
System.out.printf("나이: %s\n", c.age);
}
}
/* Cat 클래스 */
class Cat {
String name; // 이름
String breeds; // 품종
int age; // 나이
void claw() {
System.out.println("할퀴기!!");
}
void meow() {
System.out.println("야옹~");
}
}
3. 또 다른 객체 만들기
/* 메인 클래스 */
public class BicycleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 자전거 객체 생성
Bicycle b1 = new Bicycle();
// 객체 필드값 초기화
b1.name = "로드형 자전거";
b1.weight = 7.25;
b1.price = 326000;
// 객체 정보 출력
System.out.printf("b1->{%s, %.2f, %d}\n", b1.name, b1.weight, b1.price);
/* 1. 새 자전거 객체 b2를 생성하시오. */
Bicycle b2 = new Bicycle();
/* 2. b2 객체의 필드를 초기화하시오. */
b2.name = "산악형 자전거";
b2.weight = 10.68;
b2.price = 429000;
/* 3. b2 객체 정보를 출력하시오. */
System.out.printf("b2->{%s, %.2f, %d}\n", b2.name, b2.weight, b2.price);
}
}
/* 자전거 클래스 */
class Bicycle {
/* 필드 */
String name; // 이름
double weight; // 무게
int price; // 가격
/* 메소드 */
void move() {
System.out.println("자전거를 타고 이동합니다.");
}
void horn() {
System.out.println("따르르릉! 지나갈게요~");
}
}
4. 인스턴스 메소드 호출
public class CatTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 고양이 객체 c1 생성
Cat cat1 = new Cat();
Cat cat2 = new Cat();
// 메소드 호출
cat1.meow();
cat2.meow();
/* 1. 할퀴기 메소드를 호출하시오. */
cat1.claw();
cat2.claw();
}
}
/* 고양이 클래스 */
class Cat {
/* 필드(상태) */
String name; // 이름
String breeds; // 품종
int age; // 나이
/* 메소드(동작) */
void meow() {
System.out.println("야옹~");
}
void claw() {
/* 2. 할퀴기 메소드를 완성하시오. */
System.out.println("할퀴기!! 슥샥!");
}
}
5. 클래스 스코프
public class CatTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 두 고양이 객체 생성
Cat cat1 = new Cat();
Cat cat2 = new Cat();
// 객체 필드 초기화
cat1.name = "네로";
cat2.name = "나비";
// 두 고양이의 야옹~
cat1.meow();
cat2.meow();
// 두 고양이의 할퀴기!
cat1.claw();
cat2.claw();
}
}
/* 고양이 클래스 */
class Cat {
/* 필드(상태) 영역 */
String name; // 이름
String breeds; // 품종
int age; // 나이
/* 메소드(동작) 영역 */
void meow() {
System.out.printf("[%s]의 야옹~\n", name);
}
void claw() {
/* 1. claw 메소드를 완성하시오. */
System.out.printf("[%s]의 할퀴기! 샥샥~\n", name);
}
}
6. 메소드 스코프
public class DrinkMachineTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 객체 생성
DrinkMachine machine1 = new DrinkMachine();
DrinkMachine machine2 = new DrinkMachine();
// 음료 뽑기
machine1.pushButton(1);
machine2.pushButton(2);
// 음료 확인
machine1.printOutput();
machine2.printOutput();
}
}
class DrinkMachine {
/* 필드 */
String output;
/* 메소드 */
void pushButton(int num) {
String[] drinks = {"콜라", "사이다", "맥주"};
output = drinks[num];
}
void printOutput() {
System.out.println(output);
}
}
7. 리뷰 : 정사각형 클래스
public class SquareTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 객체 생성 */
Square s = new Square();
/* 필드 초기화(값 변경) */
s.length = 4;
int area = s.area();
/* 결과 출력 */
System.out.printf("한 변의 길이가 4인 정사각형의 넓이: %d", area);
}
}
/* 정사각형 클래스 구현 */
class Square {
int length;
int area() {
return length * length;
}
}
강의 출처 : cloudstudying.kr/lectures/195
'Study > Java & Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 11강 레퍼런스와 static편 학습 내용 보내드립니다. (0) | 2021.02.25 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 10강 생성자 호출과 정의 (0) | 2021.02.25 |
| [Python Study] 2. 두번째 데이터 타입, String (0) | 2019.01.03 |
| [Python Study] 1. 첫번째 데이터 타입, Number (0) | 2019.01.03 |
| [Java Study]6. 성적처리 프로그램 (print부터 클래스 변수까지) (0) | 2018.02.11 |


